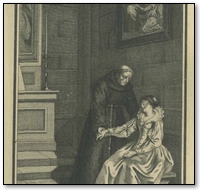
the Man of Tours and his Serving-maid in The Snow
The Heptameron - Day 5 - Tale 45 - the Man of Tours and his Serving-maid in The Snow
Summary of the Fifth Tale Told on the Fifth of the Heptameron
Tale 45 of the Heptameron

In the city of Tours dwelt a man of shrewd and sound understanding, who was upholsterer to the late Duke of Orleans, (1) son of King Francis the First; and although this upholsterer had, through sickness, become deaf, he had nevertheless lost nothing of his wit, which, in regard both to his trade and to other matters, was as shrewd as any man's. And how he was able to avail himself of it you shall hear.
He had married a virtuous and honourable woman, with whom he lived in great peace and quietness. He was very fearful of displeasing her, whilst she, on her part, sought in all things to obey him. But, for all the affection that he bore her, he was so charitably inclined that he would often give to his female neighbours that which by right belonged to his wife, though this he did as secretly as he was able.
There was in their house a very plump serving-maid with whom the upholsterer fell in love. Nevertheless, dreading lest his wife should know this, he often made show of scolding and rebuking her, saying that she was the laziest wench he had ever known, though this was no wonder, seeing that her mistress never beat her. And thus it came to pass that one day, while they were speaking about giving the Innocents, (2) the upholsterer said to his wife—
"It were a charity to give them to that lazy wench of yours, but it should not be with your hand, for it is too feeble, and in like way your heart is too pitiful for such a task. If, however, I were to make use of mine, she would serve us better than she now does."
The poor woman, suspecting no harm, begged him to do execution upon the girl, confessing that she herself had neither strength nor heart for beating her.

The husband willingly accepted this commission, and, playing the part of a stern executioner, had purchase made of the finest rods that could be found. To show, moreover, how anxious he was not to spare the girl, he caused these rods to be steeped in pickle, so that his poor wife felt far more pity for her maid than suspicion of her husband.
Innocents' Day being come, the upholsterer rose early in the morning, and, going up to the room where the maid lay all alone, he gave her the Innocents in a different fashion to that which he had talked of with his wife. The maid wept full sore, but it was of no avail. Nevertheless, fearing lest his wife should come upon them, he fell to beating the bed-post with the rods which he had with him in such wise that he barked and broke them; and in this condition he brought them back to his wife, saying—
"Methinks, sweetheart, your maid will remember the Innocents."
When the upholsterer was gone out of the house, the poor servant threw herself upon her knees before her mistress, telling her that her husband had done her the greatest wrong that was ever done to a serving-maid. The mistress, however, thinking that this merely had reference to the flogging which she believed to have been given, would not suffer the girl to finish, but said to her—
"My husband did well, and only what I have for more than a month been urging him to do. If you were hurt I am very glad to hear it. You may lay it all at my door, and, what is more, he did not even do as much as he ought to have done."
The serving-maid, finding that her mistress approved of the matter, thought that it could not be so great a sin as she had imagined, the more so as it had been brought to pass by a woman whose virtue was held in such high repute. Accordingly she never afterwards ventured to speak of it.
Her master, however, seeing that his wife was as content to be deceived as he was to deceive her, resolved that he would frequently give her this contentment, and so practised on the serving-maid, that she wept no more at receiving the Innocents.
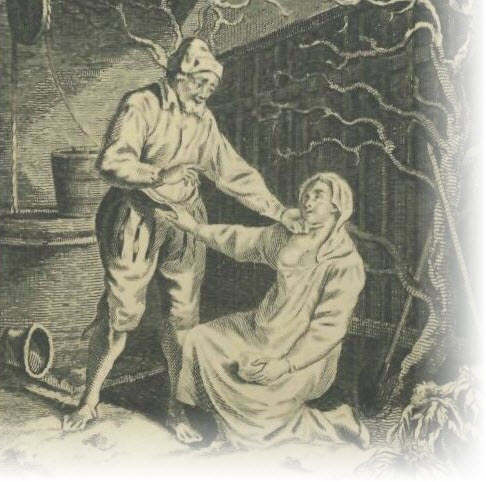
He continued this manner of life for a great while, without his wife being any the wiser, until there came a time of heavy snow, when, having already given the girl the Innocents on the grass in his garden, he was minded to do the same in the snow. Accordingly, one morning before any one in the house was awake, he took the girl clad in nothing but her shift to make the crucifix in the snow, and while they were pelting each other in sport, they did not forget the game of the Innocents.
This sport, however, was observed by one of their female neighbours who had gone to her window, which overlooked the garden, to see what manner of weather it was, and so wrathful was she at the evil sight, that she resolved to tell her good gossip of it, to the end that she might no longer suffer herself to be deceived by a wicked husband or served by a wanton jade.
After playing these fine pranks, the upholsterer looked about him to see whether any one could perceive him, and to his exceeding annoyance observed his neighbour at her window. But just as he was able to give any colour to his tapestry, so he bethought him to give such a colour to what he had done, that his neighbour would be no less deceived than his wife. Accordingly, as soon as he had gone back to bed again, he made his wife rise in nothing but her shift, and taking her into the garden as he had taken his serving-maid, he played with her for a long time in the snow even as he had played with the other. And then he gave her the Innocents in the same way as he had given them to the maid, and afterwards they returned to bed together.
Heptameron Story 45
When the good woman went to mass, her neighbour and excellent friend failed not to be there, and, while unwilling to say anything further, zealously begged of her to dismiss her serving-maid, who was, she said, a very wicked and dangerous wench. This, however, the other would not do without knowing why she thought so ill of the girl, and at last her neighbour related how she had seen the wench that morning in the garden with her husband.
At this the good woman fell to laughing heartily, and said—
"Eh! gossip dear, 'twas myself!"
"What, gossip? Why she wore naught but her shift, and it was only five o'clock in the morning."
"In faith, gossip," replied the good woman, "'twas myself."
"They pelted each other with snow," the other went on, "on the breasts and elsewhere, as familiarly as could be."
"Eh! gossip, eh!" the good woman replied, "'twas myself."
"Nay, gossip," said the other, "I saw them afterwards doing something in the snow that to my mind is neither seemly nor right."
"Gossip," returned the good woman, "I have told you, and I tell you again, that it was myself and none other who did all that you say, for my good husband and I play thus familiarly together. And, I pray you, be not scandalised at this, for you know that we are bound to please our husbands."
So the worthy gossip went away, more wishful to possess such a husband for herself than she had been to talk about the husband of her friend; and when the upholsterer came home again his wife told him the whole story.
"Now look you, sweetheart," replied the upholsterer, "if you were not a woman of virtue and sound understanding we should long ago have been separated the one from the other. But I hope that God will continue to preserve us in our mutual love, to His own glory and our happiness."
"Amen to that, my dear," said the good woman, "and I hope that on my part you will never find aught to blame." (3)
"Unbelieving indeed, ladies, must be the man who, after hearing this true story, should hold you to be as crafty as men are; though, if we are not to wrong either, and to give both man and wife the praise they truly deserve, we must needs admit that the better of the two was worth naught."
"The man," said Parlamente, "was marvellously wicked, for he deceived his servant on the one side and his wife on the other."
"Then you cannot have understood the story," said Hircan. "We are told that he contented them both in the same morning, and I consider it a highly virtuous thing, both for body and mind, to be able to say and do that which may make two opposites content."
"It was doubly wicked," said Parlamente, "to satisfy the simplicity of one by falsehood and the wickedness of the other by vice. But I am aware that sins, when brought before such judges as you, will always be forgiven."
"Yet I promise you," said Hircan, "that for my own part I shall never essay so great and difficult a task, for if I but render you content my day will not have been ill spent."
"If mutual love," said Parlamente, "cannot content the heart, nothing else can."
"In sooth," said Simontault, "I think there is no greater grief in the world than to love and not be loved."
"To be loved," said Parlamente, "it were needful to turn to such as love. Very often, however, those women who will not love are loved the most, while those men who love most strongly are loved the least."
"You remind me," said Oisille, "of a story which I had not intended to bring forward among such good ones."
"Still I pray you tell it us," said Simontault. "That will I do right willingly," replied Oisille.
Footnotes:
- Charles of France, Duke of Orleans, Bourbonnais, Angoumois and Châtelherault, Count of Clermont, La Marche, and Civray, Governor and Lieutenant-General of Champagne and Brie. He has been referred to in the Memoir of Queen Margaret, ante, vol. i. pp. xxxvi., xlvii.-viii. Born at St. Germain in January 1521, the Duke of Orleans took part in several military expeditions, and gave proof of much ability as a commander. He died, according to some accounts, of a pleurisy, and, according to others, of the plague, in 1545. The above story was evidently written subsequent to that date, as Queen Margaret refers to him as "the late Duke of Orleans."—L.
- Prior to the Reformation it was the custom, not only in France but throughout Europe, to whip children on the morning of Innocents' Day (December 28), in order, says Gregory in his treatise on the Boy Bishop, "that the memory of Herod's murder of the Innocents might stick the closer." This custom (concerning which see Haspinian, De Orig. Festor, Christianor. fol. 160) subsequently degenerated into a jocular usage, so far as the children were concerned, and town-gallants and country-swains commonly sought to surprise young women in bed, and make them play the part of the Innocents, more frequently than otherwise to the loss of their virtue. A story is told of a French nobleman who in taking leave of some ladies to join a hunting party, heard one of them whisper, "We shall sleep at our ease, and pass the Innocents without receiving them." This put the nobleman, a certain Seigneur du Rivau, on his mettle. "He kept his appointment," we are told, "galloped back twenty leagues at night, arrived at the lady's house at dawn on Innocents' Day, surprised her in bed, and used the privilege of the season." (Bonn's Heptameron, p. 301). Verses illustrative of the custom will be found in the works of Clement Marot, Jannet's edition, 1868, vol iii. p. 7, and in those of Cholières, Jouaust's edition, 1879, vol. i. p. 224-6.—L. and Ed.
- This tale is accounted by most critics and commentators to be the best in the Heptameron. Dunlop thinks it may have been borrowed from a fabliau composed by some Trouvère who had travelled in the East, and points out that it corresponds with the story of the Shopkeeper s Wife in Nakshebi's Persian Tales (Tooti Nameh). Had it been brought to France, however, in the manner suggested it would, like other tales, have found its way into the works of many sixteenth-century story-writers besides Queen Margaret. Such, however, is not the case, and curiously enough, so far as we can find, the tale, as given in the Heptameron, was never imitated until La Fontaine wrote his Servante Justifiée (Contes, livre ii. No. vi.), in the opening lines of which he expressly acknowledges his indebtedness to the Queen of Navarre.—Ed.
Online Edition of the Heptameron
This is the Heptameron of Marguerite de Navarre
Other Sites: CruikshankArt.com · Dante's Inferno · Book-Lover.com · Canterbury Tales ·
This site is created by the Heptameron Information Society.